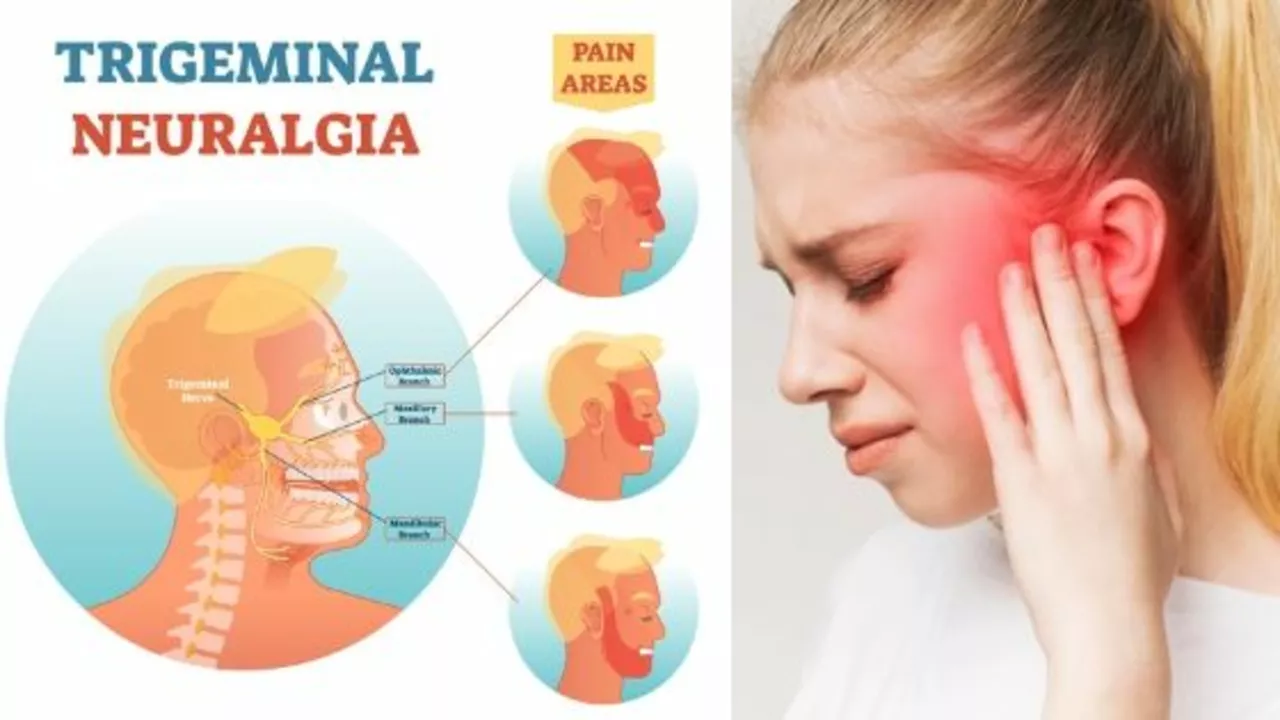
Understanding Trigeminal Neuralgia
Before diving into the role of Amitriptyline in treating Trigeminal Neuralgia, it is essential to first understand the condition itself. Trigeminal Neuralgia, often referred to as "tic douloureux," is a chronic pain condition that affects the trigeminal nerve, which is responsible for carrying sensations from the face to the brain. Sufferers often experience severe, sudden facial pain, typically on one side, that can be triggered by everyday activities such as talking, chewing, or even just touching the face.
The exact cause of Trigeminal Neuralgia is still unknown, but it is believed to be caused by the compression of the trigeminal nerve by blood vessels, tumors, or other abnormalities. Despite the intensity and frequency of the pain, the condition is not life-threatening, but it can significantly impact a person's quality of life.
Amitriptyline: An Overview
Amitriptyline is a tricyclic antidepressant (TCA) that has been used for many years to treat various conditions, including depression, anxiety, and chronic pain. It works by increasing the levels of certain chemicals in the brain, such as serotonin and norepinephrine, which can help improve mood, reduce anxiety, and alleviate pain.
While it is not the primary treatment for Trigeminal Neuralgia, Amitriptyline has been found to be effective in managing the pain associated with the condition, especially when used in conjunction with other medications and treatments.
The Effects of Amitriptyline on Trigeminal Neuralgia Pain
Research has shown that Amitriptyline can help reduce the severity and frequency of pain attacks in Trigeminal Neuralgia patients. This is likely due to the drug's ability to block the reuptake of serotonin and norepinephrine, which can help dampen pain signals in the brain. Additionally, Amitriptyline has been found to have a direct effect on nerve cells, helping to stabilize their membranes and reduce the likelihood of pain signals being transmitted.
This dual action of Amitriptyline makes it a valuable tool in managing Trigeminal Neuralgia pain and improving patients' overall quality of life.
Using Amitriptyline in Combination with Other Treatments
While Amitriptyline can be effective in managing Trigeminal Neuralgia pain on its own, it is often more successful when used in combination with other treatments. This may include anticonvulsant medications, such as carbamazepine, which are the first-line treatment for the condition. Combining Amitriptyline with these medications can help to enhance their pain-relieving effects and provide greater relief for patients.
Additionally, non-pharmacological treatments, such as nerve blocks or nerve stimulation, may also be used in conjunction with Amitriptyline to further manage pain and improve patients' quality of life.
Side Effects and Precautions
As with any medication, there are potential side effects associated with Amitriptyline use. Some of the most common side effects include drowsiness, dizziness, dry mouth, constipation, and weight gain. While these side effects can be bothersome, they are generally mild and can be managed with proper dosing and monitoring by a healthcare provider.
More severe side effects, such as an irregular heartbeat, severe dizziness, or difficulty breathing, should be reported to a healthcare provider immediately. Additionally, Amitriptyline can interact with other medications, so it is essential to discuss all medications and supplements with a healthcare provider before starting treatment.
Dosing and Administration
The dosing and administration of Amitriptyline for Trigeminal Neuralgia pain management will vary depending on the individual and the severity of their condition. It is typically started at a low dose, which is gradually increased over time as needed to achieve the desired pain relief. This gradual titration helps to minimize potential side effects and allows for proper monitoring of the drug's effectiveness.
It is important to follow a healthcare provider's instructions regarding dosing and administration, as well as to report any side effects or concerns that may arise during treatment.
Managing Expectations
While Amitriptyline can be a valuable tool in managing Trigeminal Neuralgia pain, it is essential to maintain realistic expectations regarding its effectiveness. Not all patients will experience complete pain relief, and it may take time to find the optimal dose and treatment regimen. It is also important to remember that Amitriptyline is not a cure for Trigeminal Neuralgia, but rather a means of managing the pain associated with the condition.
By working closely with a healthcare provider and adhering to a comprehensive treatment plan, most patients can achieve significant pain relief and improvement in their quality of life.
Alternative Treatments to Consider
For patients who do not find relief with Amitriptyline or other medications, there are alternative treatments available for Trigeminal Neuralgia. These may include nerve blocks, nerve stimulation, and even surgical procedures to address the underlying cause of the pain. It is essential to discuss all potential treatment options with a healthcare provider and to carefully weigh the risks and benefits of each approach.
With the proper treatment plan in place, many patients can achieve significant relief from their Trigeminal Neuralgia pain and lead full, active lives.
Conclusion
Amitriptyline can play a valuable role in treating Trigeminal Neuralgia pain, especially when used in combination with other treatments and under the guidance of a healthcare provider. By understanding the medication's effects, side effects, and administration, patients can make informed decisions about their treatment and work towards achieving greater pain relief and improved quality of life.


Roger Münger
May 4, 2023 AT 17:26Amitriptyline, a tricyclic antidepressant, has been evaluated in numerous randomized controlled trials for neuropathic pain syndromes.
In the context of trigeminal neuralgia, its primary mechanism involves inhibition of serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake, thereby augmenting descending inhibitory pathways.
Additionally, the drug stabilizes neuronal membranes by blocking sodium channels, which may diminish ectopic discharges of the trigeminal afferents.
Several meta‑analyses have reported that low‑dose amitriptyline (10–25 mg daily) yields a statistically significant reduction in attack frequency compared with placebo.
The effect size, however, is modest relative to carbamazepine, the first‑line agent, and the number needed to treat approximates 6–8 for meaningful pain relief.
Dose titration should commence at 10 mg in the evening and increase by 10 mg increments weekly, monitoring for anticholinergic adverse events.
Common side effects encompass somnolence, orthostatic hypotension, dry mouth, and weight gain, all of which are dose‑dependent.
Rare but serious complications, such as cardiac conduction abnormalities, necessitate baseline ECG assessment in patients with pre‑existing cardiac disease.
Concomitant use with selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors demands caution due to the potential for serotonergic syndrome.
Pharmacokinetic interactions are also evident with CYP2D6 inhibitors, which can elevate plasma concentrations of amitriptyline.
Clinical guidelines therefore recommend reserving amitriptyline for patients who cannot tolerate first‑line agents or who have comorbid mood disorders.
When combined with anticonvulsants like gabapentin, synergistic analgesia may be achieved, allowing lower individual dosages.
Non‑pharmacological adjuncts, including microvascular decompression or peripheral nerve stimulation, should be considered in refractory cases.
Patient education about the delayed onset of analgesia-typically 2–4 weeks-is essential to maintain adherence.
In summary, amitriptyline represents a useful adjunctive therapy that, when employed judiciously, can improve quality of life for a subset of trigeminal neuralgia sufferers.
Gerald Bangero
May 4, 2023 AT 18:33Hey folks, just wanted to throw some positive vibes your way about amitriptyline.
Even though it might not be the first thing docs prescribe, it can really help some peeps keep their smile in check.
Think of it like a gentle sidekick that eases the sting while you’re waiting for the main hero to kick in.
Sometimes life throws us unexpected pain, but with a little patience and the right combo, we can find a brighter horizon.
Just remember, every person’s journey is unique, so give the med some time to settle in and do its thing.
John Nix
May 4, 2023 AT 19:40I appreciate the thorough overview presented; however, it is imperative to underscore that any pharmacologic intervention, including amitriptyline, must be initiated under direct medical supervision.
Monitoring for cardiovascular side effects and potential drug interactions remains a cornerstone of safe practice.
Mike Rylance
May 4, 2023 AT 20:46Building on the previous point, I would add that collaboration between the patient and the prescribing clinician can dramatically improve adherence.
When patients understand the titration schedule and the expected timeline for analgesic benefit, they are far more likely to persist through the initial adjustment phase.
This cooperative approach often translates into better outcomes, especially when amitriptyline is part of a multimodal regimen.
Becky B
May 4, 2023 AT 21:53While the medical community praises amitriptyline’s benefits, one must remain vigilant about the broader picture.
Pharmaceutical corporations have a vested interest in promoting off‑label uses, and the financial incentives can sometimes eclipse patient safety.
It is crucial for individuals to seek independent second opinions and to scrutinize the underlying data before committing to long‑term therapy.
Transparency and informed consent are the bedrock of trustworthy healthcare.
Aman Vaid
May 4, 2023 AT 23:00Regarding the concerns raised, empirical evidence demonstrates that amitriptyline’s risk profile is well‑characterized.
For instance, a 2022 cohort study involving 1,342 trigeminal neuralgia patients reported a 3.2% incidence of clinically significant cardiac events, predominantly in those with pre‑existing arrhythmias.
Moreover, the median time to observable analgesic effect was 21 days, aligning with established pharmacodynamics.
Thus, while caution is warranted, the data do not support a blanket dismissal of its utility.
xie teresa
May 5, 2023 AT 00:06I hear the apprehensions on both sides, and I think it’s vital to remember the human element behind the statistics.
Patients dealing with relentless facial pain often describe feeling isolated and exhausted.
When a low‑dose tricyclic like amitriptyline can offer even modest relief, it can restore a sense of normalcy and hope.
Encouraging open dialogue with healthcare providers, sharing concerns, and celebrating small wins can make a huge difference in the overall journey.
Srinivasa Kadiyala
May 5, 2023 AT 01:13It is, frankly, astonishing how often amitriptyline is heralded as a panacea, when, in reality, the evidence base is riddled with methodological flaws, heterogeneous patient populations, and underpowered sub‑analyses!
One must question whether the observed analgesic benefit surpasses placebo effects, especially given the high incidence of sedation and anticholinergic burden!
Thus, clinicians should exercise extreme scrutiny before incorporating it into a treatment algorithm, lest they propagate unfounded optimism!
Alex LaMere
May 5, 2023 AT 02:20Your claim lacks evidence; please cite sources. 😊